Last Updated on November 26, 2025
What if you could access all your business data—from cloud platforms, databases, and apps—without ever moving it? That’s the magic of data virtualization, the silent engine powering some of the fastest, smartest companies in 2025.
While others are still building costly pipelines and duplicating data, forward-thinking businesses are tapping into real-time insights with just a few clicks with data virtualization.
But how exactly does it work? And why is everyone suddenly talking about it?
Keep reading—you’re about to uncover the future of data access.
Why Data Virtualization Matters More Than Ever in 2025
In 2025, businesses are generating and consuming more data than ever before—but accessing that data in real time across fragmented systems remains a major challenge. As organizations adopt cloud platforms, SaaS tools, IoT devices, and edge computing, their data becomes increasingly distributed, complex, and siloed.
Data virtualization solves this fragmentation without the time, cost, and complexity of traditional data integration methods. It also empowers organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions or regulatory requirements, ensuring they remain agile and compliant in an increasingly dynamic environment.
Data virtualization is being adopted across various industry sectors, from healthcare and finance to retail and manufacturing, due to its versatility and impact. Here are some of the top factors driving this trend:
1. Explosion of Cloud & Hybrid Environments
Most organizations now store data across multiple clouds and on-prem systems. Data virtualization provides a single access layer across all these sources—making it possible to work with all that data without consolidation or migration.
2. Real-Time Decision-Making Is No Longer Optional
Markets today move too fast. Traditional ETL processes (which can take hours or days) simply can’t keep up. Data virtualization enables on-demand, real-time access to insights, so leaders can act immediately—not after the fact.
3. Data Democratization Is Becoming a Priority
Modern businesses need data access beyond IT teams. With data virtualization, non-technical users can query data via familiar BI tools, without depending on engineering teams to prepare or deliver it.
4. Regulatory Compliance & Governance Requirements
With tightening global regulations (like GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, etc.), organizations must know where their data lives and how it’s used. Data virtualization makes it easier to enforce governance – and thereby, ensure compliance – without duplicating sensitive data.
What is Data Virtualization, Really?
Data virtualization is a data integration technology that allows users to access, manage, and query data from multiple sources without physically moving or copying it.
Instead of consolidating data into a single repository, it creates a virtual layer that connects to cloud platforms, databases, SaaS apps, and files in real time, and provides a unified, logical view of data from multiple sources.
Data virtualization eliminates the need to impose a single data model across all systems, allowing organizations to maintain source data formats, as well as moving data between systems.
This means businesses can view and analyze their data as if it’s in one place, while it stays in its original locations – secure and unchanged.
What Data Sources Can Be Virtualized?
Modern data virtualization platforms can connect to and integrate with a wide range of data sources, including both structured and unstructured data and heterogeneous data formats and systems. These include:
- Relational Databases: Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, IBM Db2
- Cloud Storage & Cloud Data Warehouses: Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Azure Synapse Analytics
- Enterprise Applications & SaaS Platforms: Salesforce, SAP, Workday, Microsoft Dynamics, NetSuite, ServiceNow
- Flat Files & Semi-Structured Data: CSV, Excel, XML, JSON documents, files stored on local or cloud file systems, data lakes using HDFS or cloud-native formats
- APIs & Web Services: REST APIs, SOAP services, GraphQL endpoints, real-time data feeds from partners or providers
- Big Data Platforms: Apache Hadoop, Cloudera, Hortonworks, Databricks
- Streaming Data Sources: Apache Kafka, Amazon Kinesis, Azure Event Hubs, MQTT brokers (for IoT data)
- Enterprise Data Warehouses: Teradata, IBM Netezza, Vertica, Exadata
Why Virtualize Your Data? Top 5 Benefits of Data Virtualization
Data virtualization has become a key asset in today’s cloud-first, multi-platform environments. Here are some of its top benefits, especially for organizations aiming to modernize their data strategy.
1. Real-Time Access
Data virtualization enables instant access to live data across multiple systems—databases, cloud platforms, APIs—without needing to copy or move it. This real-time capability supports faster decision-making and up-to-date reporting.
2. No ETL Bottlenecks
Unlike ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes that require significant time and infrastructure, data virtualization eliminates the need for physical data replication. This drastically reduces costs, simplifies data workflows, and shortens project timelines.
3. Lower Infrastructure and Storage Costs
By accessing data virtually instead of storing redundant copies, organizations reduce the need for extra storage, servers, and data warehouses. This leads to significant cost savings—especially for large enterprises managing high-volume data environments.
4. Improved Data Governance and Security
Data virtualization keeps data in its original source, making it easier to maintain control, apply access permissions and quality checks, and ensure compliance.
Tools like DataMatch Enterprise support this process behind the scenes by enhancing data quality, profiling inconsistencies, cleaning, deduplicating, and matching records across systems without data ingestion or physical consolidation.
5. Empowers Self-Service and Business Agility
Business users (not just IT teams) can query and explore data using BI tools (like Tableau, Power BI, or Excel) via the virtualized layer. This self-service model reduces dependency on developers, encourages innovation, and allows faster adaptation to market needs.
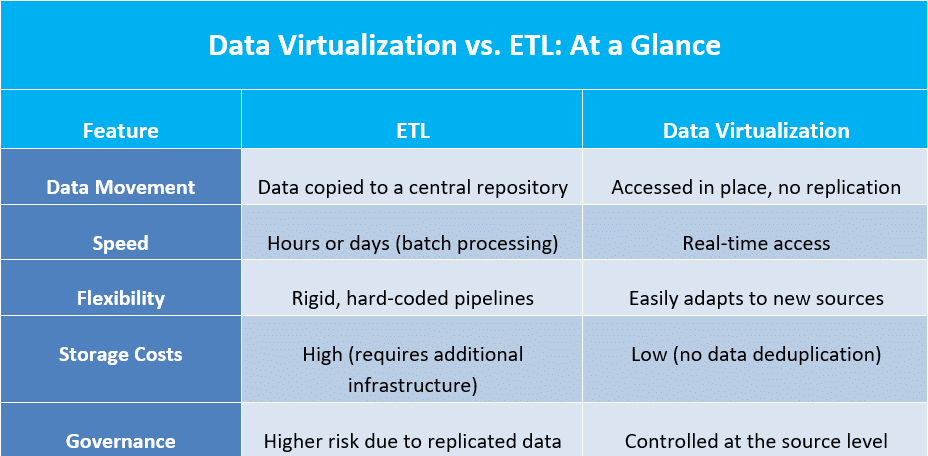
Data Virtualization vs. Traditional Data Integration
While traditional data integration methods like ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) have long been the standard, data virtualization is now emerging as a modern, more agile solution to how organizations access and manage their data.
Traditional ETL involves extracting data from multiple sources, transforming it into a common format, and loading it into a central repository such as a data warehouse.
Data virtualization, on the other hand, creates a virtual layer that allows users to access and query data from multiple sources in real time, without physically moving or replicating the data.
Unlike data federation, which integrates data from heterogeneous sources without requiring a unified data model and emphasizes real-time access and data consistency, data virtualization provides a unified virtual view for more seamless access and analysis.
Understanding the differences between these two approaches is critical for businesses making digital transformation decisions in 2025.
Traditional Data Integration (ETL)
Traditional data integration or ETL method is ideal for batch processing and historical reporting but comes with several limitations:
- Data latency: ETL works on scheduled batches, meaning there’s always a risk of insights being slightly outdated.
- High infrastructure costs: Requires storage, processing power, and pipeline maintenance.
- Slow to adapt: Adding or modifying data sources demands time and development effort.
- Risk of data duplication: Replicating sensitive data increases security and compliance risks.
Data Virtualization
Data virtualization addresses the limitations of traditional ETL by providing:
- Real-time access: Users work with live data, ideal for dashboards, reporting, and agile decision-making.
- No replication: Reduces storage needs, simplifies compliance, and improves data governance.
- Greater flexibility: Easily connects to new data sources without rebuilding pipelines.
- Lower operational overhead: Fewer moving parts mean reduced maintenance costs and faster time-to-insight.
While virtualization removes the need for traditional ETL, ensuring high data quality across connected sources remains crucial. That’s why many teams pair it with tools like DataMatch Enterprise to quietly improve consistency, resolve duplicates, and enhance record matching before analytics or reporting—ensuring the data accessed virtually is both real-time and reliable.
How Data Virtualization Works? A 4-Step Process
A data virtualization platform connects to multiple data sources and presents a single, queryable interface for analytics and reporting. Here are the steps involved in the process:
1. Connect to Data Sources
- The virtualization platform uses prebuilt connectors to access structured and unstructured data from sources like SQL databases, APIs, cloud services (AWS, Azure), and SaaS platforms (Salesforce, Snowflake).
- This connection is non-invasive—data stays at the source.
2. Create a Virtual Schema (Metadata Layer)
- The platform generates a metadata layer that maps the data models from all connected systems.
- It then presents the data as if it’s coming from one single, unified source.
Many organizations use tools like DataMatch Enterprise at this stage to clean, deduplicate, and match records before or alongside virtual schema generation. This ensures the metadata reflects high-quality, harmonized, accurate data.
3. Run Optimized Real-Time Queries
- When a user or tool submits a query (e.g., via SQL, BI dashboards), the system breaks it into sub-queries.
- Each sub-query is sent to the relevant data source, and results are federated (combined) in real time for immediate insights and analysis.
4. Apply Governance and Security Measures
- The platform applies governance and security measures, like role-based access, data masking, encryption, and auditing, without storing data in a central repository.
The Role of Virtualization in Modern Industry Operations: Data Virtualization Use Cases
Data virtualization is no longer just a buzzword—it’s a strategic solution powering critical operations across industries. From retail and finance to healthcare and logistics, organizations are leveraging data virtualization to gain real-time insights, reduce costs, and streamline data access.
Let’s look at some real-life examples of how businesses are using data virtualization—and the measurable impact it’s having.
Healthcare: Integrating Patient Data Across Systems
- Creates a real-time, unified view of patient data from EHR, billing, lab, and imaging systems
- Enables clinicians to access up-to-date patient information during care without waiting for batch uploads
- Improves coordination between departments (e.g., ER, radiology, pharmacy)
- Supports HIPAA compliance with enhanced data security by keeping sensitive data at its original source while still being accessible
- Enhances population health reporting and public health data initiatives
Finance: Real-Time Risk Monitoring & Fraud Detection
- Provides real-time access to customer data across departments (loans, credit cards, investments)
- Improves risk modeling and fraud prevention and enables faster fraud detection using up-to-date data from multiple sources
- Simplifies regulatory reporting by querying live data instead of maintaining redundant data warehouses
Manufacturing: Supply Chain Optimization
- Combines real-time sensor data with inventory and demand forecasts to optimize production
- Provides a unified view of supply chains, reducing delays and bottlenecks
- Allows executives to monitor operations and KPIs across global plants from a single dashboard
- Reduces downtime by integrating predictive maintenance data with existing systems
Retail: Powering Smarter Inventory & Customer Engagement
- Syncs data from different sources – eCommerce sites, physical stores, supply chains, marketing platforms, and POS systems
- Delivers a unified view of inventory across online and in-store channels in real time
- Helps personalize promotions by combining data from loyalty programs, CRM, and sales
- Speeds up reporting for regional managers by pulling live data from multiple systems
- Supports demand forecasting and replenishment planning with greater accuracy
What’s Next for Data Virtualization?
As data environments become increasingly complex and decentralized, data virtualization is evolving from a niche integration method into a core component of enterprise data strategy. Its ability to provide real-time access to distributed data without replication positions it as a foundational layer for future-ready data architecture.
Here are the key directions in which data virtualization is heading.
1. Integration with AI/ML
Virtualization allows artificial intelligence and machine learning models to consume up-to-date data directly from the source, minimizing delays and reducing preparation time.
Data virtualization platforms are expected to increasingly support AI workloads by offering AI-optimized data views, simplifying data wrangling and improving model accuracy.
2. Enabling Data Fabric & Data Mesh Architectures
As organizations move away from centralized data lakes toward decentralized frameworks like data mesh and data fabric, data virtualization serves as the logical access layer that binds disparate data domains together.
By enabling self-service access, federated governance, and reusable data assets, virtualization supports scalable, domain-driven architectures that align with modern enterprise needs.
3. Advancing Real-Time Governance and Compliance
With the regulatory landscape becoming more stringent , data virtualization is increasingly incorporating real-time compliance capabilities, including:
- Role-based data access
- Dynamic data masking
- In-flight auditing and logging
- Policy enforcement at the source level
These enhancements allow organizations to maintain regulatory compliance while ensuring agile access to sensitive information.
4. Growing Adoption Among Mid-Sized Businesses
While previously more common in large enterprises, data virtualization is becoming increasingly accessible to small and medium-sized businesses. This is due to the rise of cloud-native solutions, flexible pricing models, and low-code integration tools.
More businesses are now using virtualization to streamline reporting, improve data governance, and accelerate digital transformation—without investing in large infrastructure.
Make Real-Time Access Work for You with a Data Quality Tool
The rise of data virtualization represents a shift in how organizations think about data—not as something to be collected and stored, but as something to be accessed, connected, and acted upon in the moment it’s needed. It offers a model where agility, governance, and performance can coexist. As the demand for real-time intelligence grows, businesses that embrace this shift early will not only improve how they use data—but also how they compete.
But to unlock the value of your virtualization platform, you can’t afford to overlook data quality. Pair it up with the right data quality tool to ensure the information you access virtually is clean, consistent, and ready for action.
Download a free trial or book a personalized demo with our expert today to see how DataMatch Enterprise helps ensure your real-time decisions are based on clean, reliable information – not guesswork.