Data Ladder vs. Databricks for Data Matching
Organizations dealing with vast amounts of data require reliable, transparent, and efficient data matching solutions to ensure data integrity and accuracy. While Databricks serves as a powerful data repository and processing platform, it lacks native data matching and entity resolution capabilities. To achieve data matching within Databricks, users must integrate third-party solutions such as Zingg.
In contrast, Data Ladder’s DataMatch Enterprise (DME) is a purpose-built, comprehensive data matching solution that offers transparency, high accuracy, and deep control over data processing.




Understanding Your Data: Transparency & Clarity
Data Ladder’s DataMatch Enterprise (DME) outperforms competitors in data matching accuracy, primarily due to its unmatched transparency and clarity in the data matching process. Organizations need to not only understand their data but also have visibility into what is happening to their data, including:





Unlike black-box AI solutions, DME provides full visibility into matching logic, offering businesses complete control over their data processing workflows. This means organizations can trust their matching results, fine-tune their processes based on real insights,and make informed decisions that improve overall data quality.
Key Features Comparison: Data Ladder vs. Databricks


| Native Data Matching | Yes | No (Requires Zingg) |
| Understanding Your Data | Full transparency in matches, audit trails, and clear data profiling. | Black-box AI approach with limited visibilityinto matching decisions. |
| Match Accuracy | Superior, with clear percentage scores and explainability. | ML-driven, requiring iterative training with less control over the process. |
| Address Standardization | Built-in address verification and cleansing. | Requires third-party integrations. |
| Pattern Matching & AI | Advanced pattern recognition and AI enhanced matching. | Machine learning-based, but requires ongoing model training. |
| Data Cleansing & Standardization | Out-of-the-box cleansing, transformation, and standardization. | Requires custom workflows and scripts. |
| Deployment Flexibility | Subscription & perpetual licensing options. | Subscription-only model. |
| Ease of Use | Drag-and-drop UI, no coding required. | Requires scripting and ML expertise. |
| Launch Year | 2008 | 2021 (Zingg) |
Why Data Ladder Wins

 Transparency & Control
Transparency & Control
DME provides full visibility into what is happening to your data, how it is being matched, and why records are considered duplicates. The audit trail, version control, and detailed match reports ensure unmatched clarity, giving users full confidence in their data.
 Higher Accuracy with Explainability
Higher Accuracy with Explainability
Unlike Databricks + Zingg, which operates as a black-box machine learning model, DME ensures accuracy by combining exact, fuzzy, phonetic (Soundex, Metaphone), and pattern-based matching algorithms with clear percentage-based scoring.
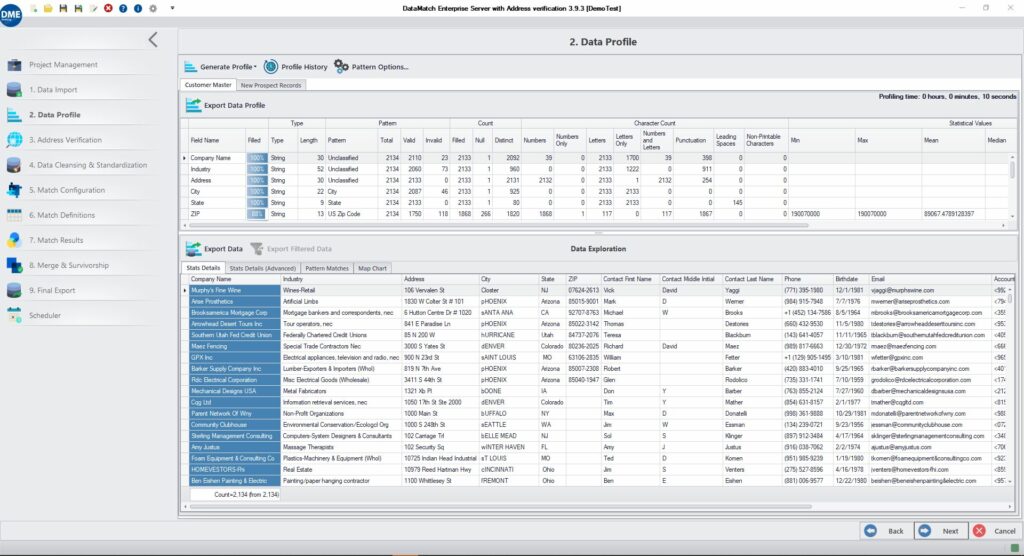
 One-Click Profiling for Immediate Insights
One-Click Profiling for Immediate Insights
DME offers an instant data profiling feature that provides quick insights into data quality issues, enabling immediate action for data improvement.
 Cost-Effective and User-Friendly
Cost-Effective and User-Friendly
With flexible annual licensing options, DME is more cost-effective than a Databricks + Zingg subscription model, which scales with data volume. DME also features an intuitive drag-and drop interface, removing the need for extensive scripting or machine learning expertise.

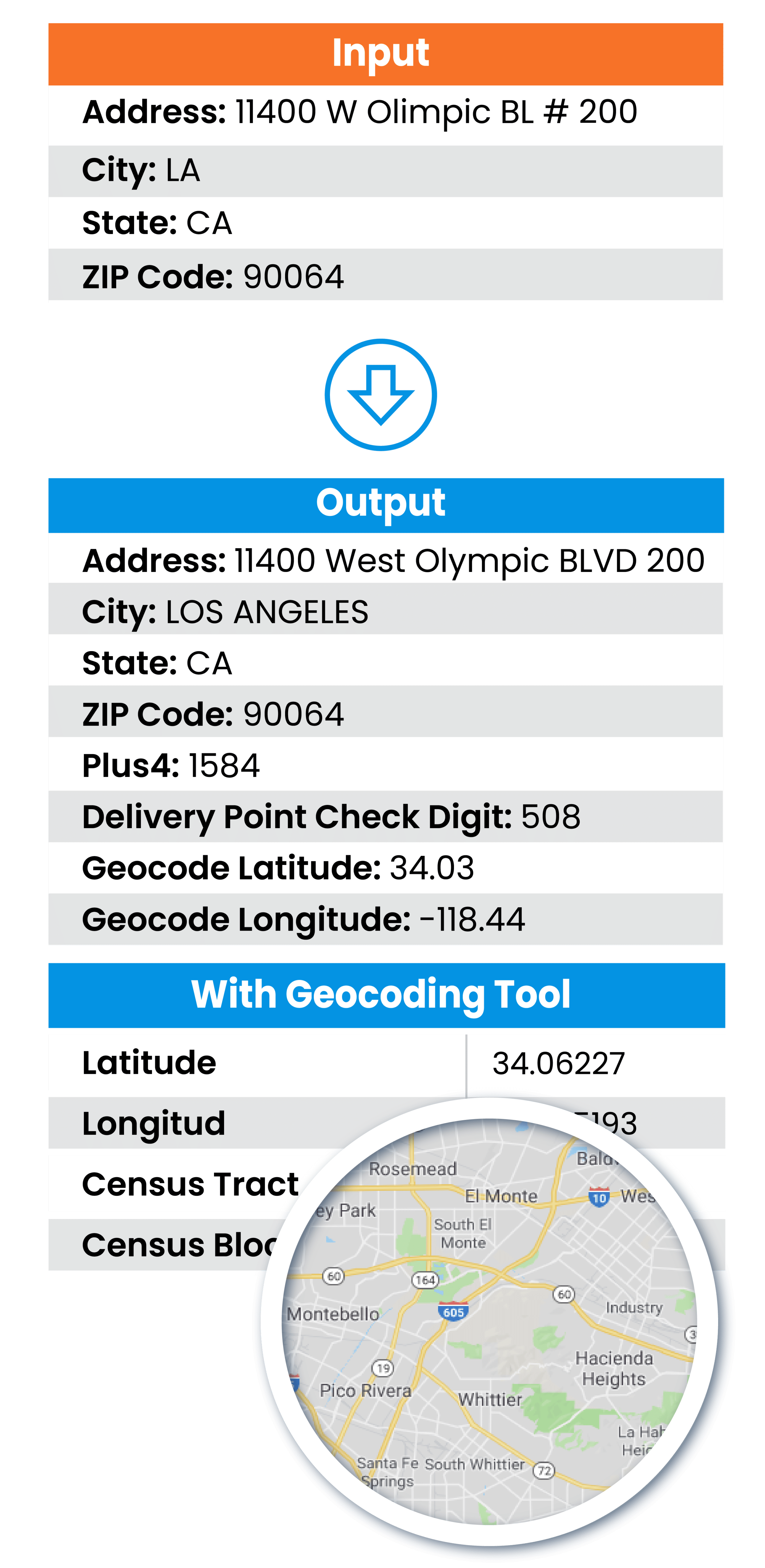
 Built-in Address Standardization & Cleansing
Built-in Address Standardization & Cleansing
DME includes robust address cleansing and standardization capabilities, ensuring accurate location-based data without requiring additional tools.
1. Data Integrity and Profiling

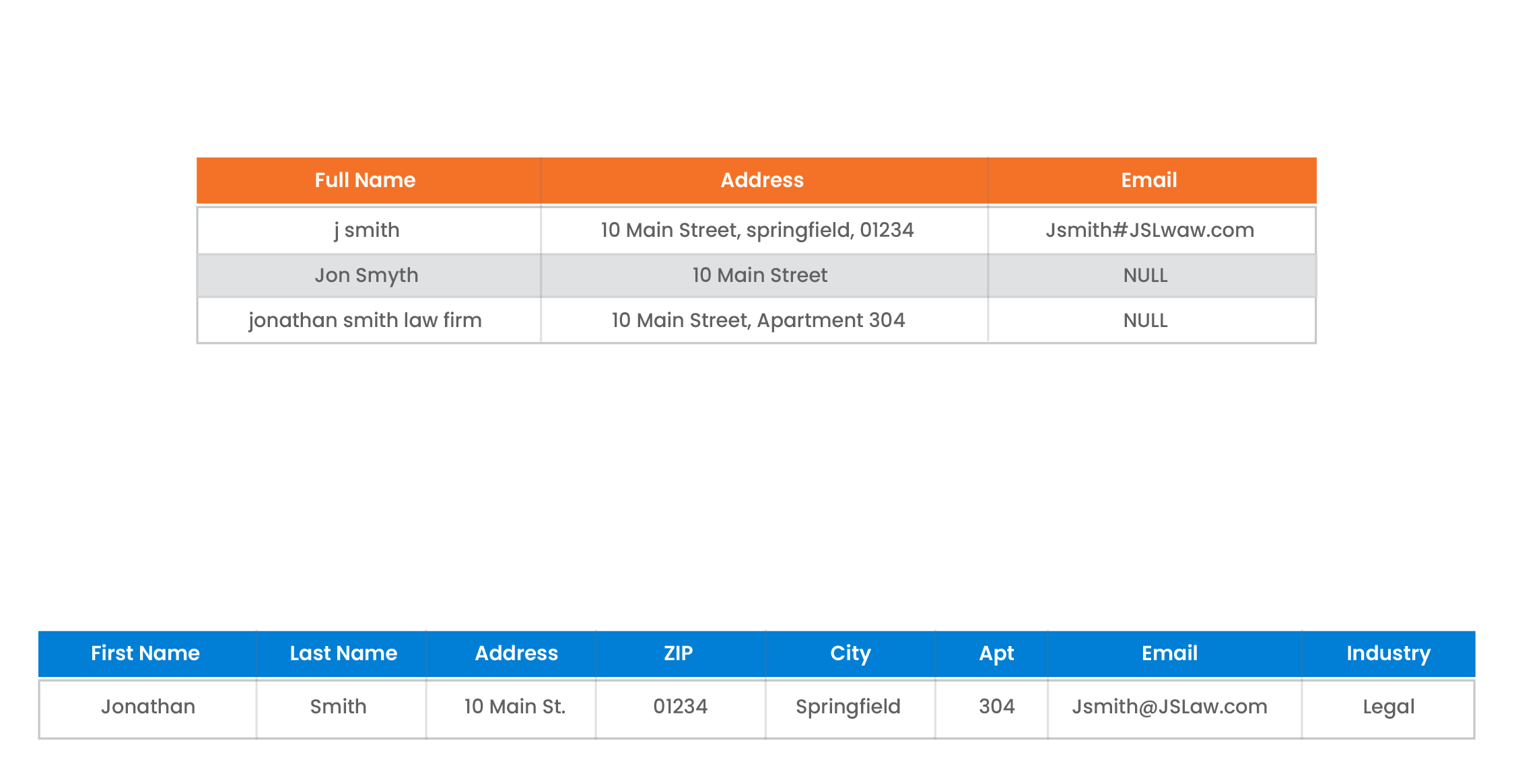
SSN and Profiling: Incorporates comprehensive SSN logic based on the US Social Security Administration recommendations, enhancing its capability to handle US-specific data such as SSNs and ZIP+4 codes.

Data Integrity: High, as it tracks manual data overwrites, preventing unauthorized changes that could compromise data integrity.

Profiling Depth: Offers deep and comprehensive data profiling, allowing for detailed analysis and cleaning of datasets before matching. Supports profiling patterns using Regular Expressions (RegEx) for a deeper dive into data types.

Cleansing Patterns: Allows parsing data into multiple columns, providing greater flexibility in data cleansing.

2. Accuracy and Grouping Quality

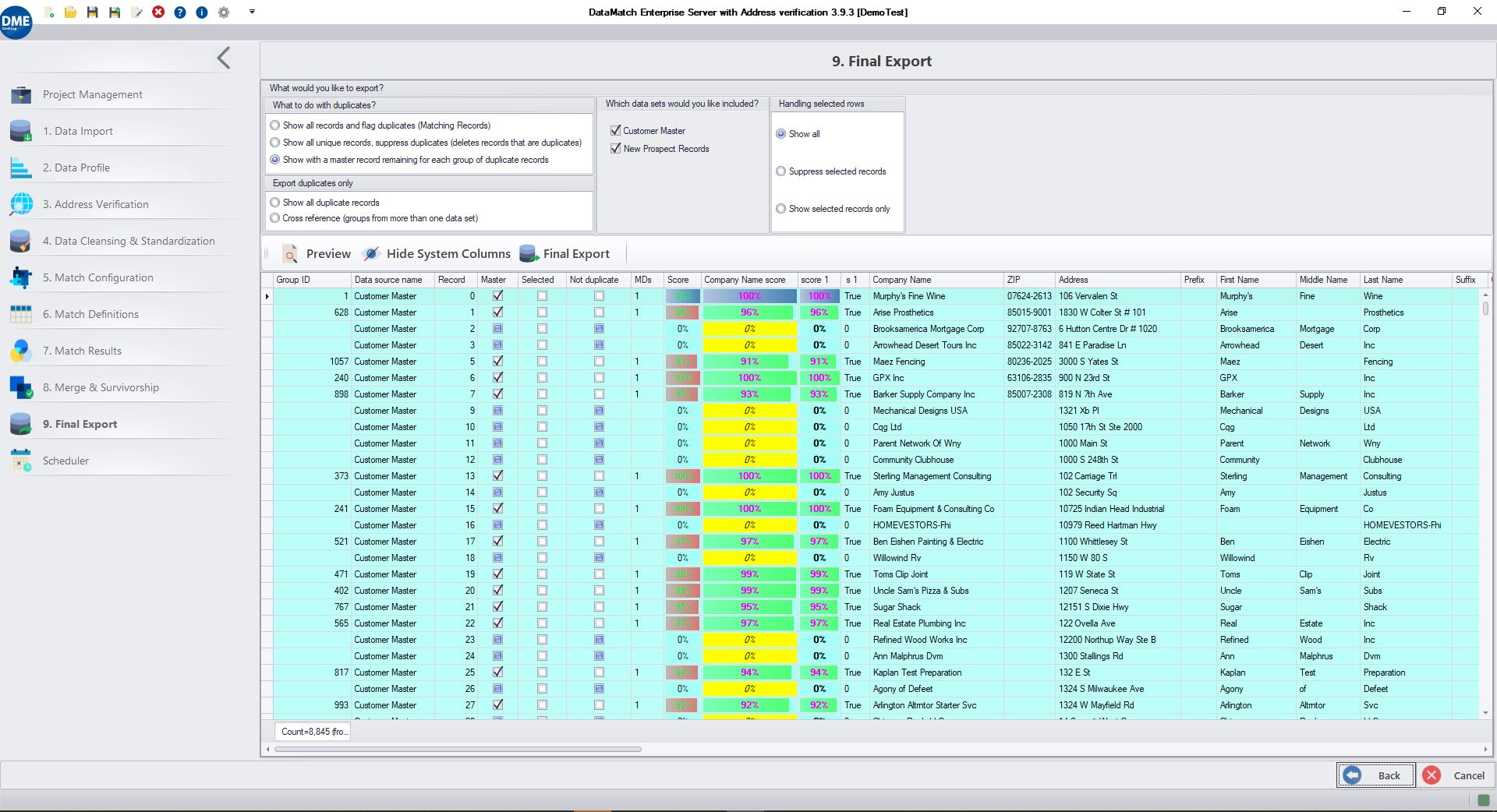
Accuracy: Demonstrates superior accuracy in matching records. For example, it found 98,430 matches and grouped them into 2,038 groups in one of the tests.

Group Quality: Better grouping accuracy, ensuring that related records are grouped correctly, which is crucial for data analysis and reporting.

Match Results Sorting and Scoring: Sorts results from highest to lowest overall score and shows scores even if the definition was not matched. Provides an option to place scores next to columns for better visibility.

3. US-Based Optimization and Fine-tuning Features for Match Accuracy

US-Based Features: Optimized for handling US-specific data, including SSNs and ZIP+4 codes. This makes it particularly suitable for US-based clients who need precise and accurate data handling.

Match Configuration: Allows one-to-many (custom config) or within-only configurations, providing flexibility in matching setups.

Mapping Rules: Conserves defined rules during remapping and supports auto-mapping for matching or merging.
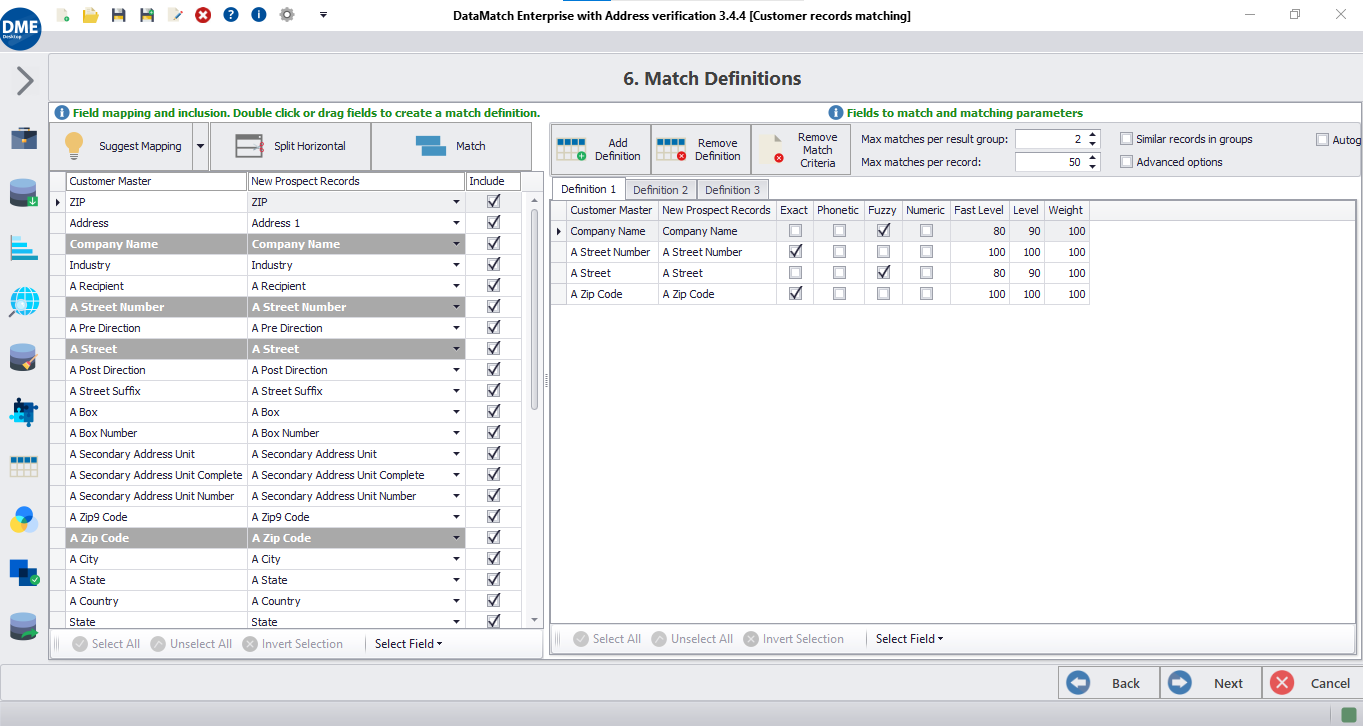
4. US-Based Optimization and Fine-tuning Features for Match Accuracy

Merge and Overwrite: Supports merging coalescence to merge the first N non-empty columns, and offers various options for overwrite/enrich (longest, shortest, max, min, merge all values).

Export Options: Includes a deduplication option (Master + Uniques) for exporting.

Match Summary Report: Includes data from the entire project, providing a comprehensive project audit.
Conclusion
For organizations prioritizing clarity, accuracy, and control over their data matching processes, Data Ladder’s DataMatch Enterprise is the superior choice. While Databricks serves as a strong data repository, it lacks built-in entity resolution and relies on third-party tools like Zingg, which introduces limitations in transparency, explainability, and flexibility. DME delivers a complete, transparent, and cost effective solution—out of the box.
Choose DataMatch Enterprise for unparalleled data matching accuracy, transparency, and ease of use.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Data Ladder best known for?
Data Ladder is best known for enterprise-grade data matching, deduplication, and entity resolution. Its platform is designed to help organizations identify, merge, and manage duplicate records across multiple systems while maintaining transparency and control over match decisions.
Is Databricks a data matching or entity resolution tool?
Databricks is not a dedicated data matching or entity resolution tool. It is a data lakehouse platform focused on large-scale analytics, data engineering, and AI workloads. Entity matching in Databricks typically requires custom code or third-party libraries.
Should I use Data Ladder or Databricks for entity resolution?
For entity resolution and data matching, Data Ladder is purpose-built and ready to use out of the box. Databricks is better suited for data processing and analytics, but entity resolution must be engineered manually or added via integrations.
Can Databricks replace a data quality or matching platform?
Databricks can support data quality initiatives at an infrastructure level, but it does not replace specialized data quality or matching platforms. Tasks like survivorship rules, golden record creation, match explainability, and review workflows are not native features of Databricks.
Does Data Ladder work alongside Databricks?
Yes. Organizations can use both platforms together, with Databricks as their data lakehouse and Data Ladder as a downstream or complementary system for cleansing, deduplication, and entity resolution before analytics or operational use.
How does Data Ladder handle explainability in data matching?
Data Ladder provides transparent match scoring, field-level similarity insights, and review workflows. This makes match decisions explainable and auditable — an important requirement for regulated industries and enterprise governance.
Can large language models (LLMs) replace traditional data matching tools?
LLMs can assist with semantic understanding and pattern discovery, but they are not replacements for deterministic, fuzzy, and probabilistic matching engines. Production-grade entity resolution still requires structured scoring, thresholds, and governance — which Data Ladder provides.
Which tool is easier for business users: Data Ladder or Databricks?
Data Ladder is designed for data stewards, analysts, and business users through visual workflows and configurable rules. Databricks primarily targets engineers and data scientists.
Can Data Ladder support master data management (MDM) initiatives?
Yes. Data Ladder supports key MDM requirements such as deduplication, entity grouping, survivorship logic, and golden record creation across customer, product, vendor, and other domains.





























 Transparency & Control
Transparency & Control Higher Accuracy with Explainability
Higher Accuracy with Explainability One-Click Profiling for Immediate Insights
One-Click Profiling for Immediate Insights Cost-Effective and User-Friendly
Cost-Effective and User-Friendly

